-
Research Article
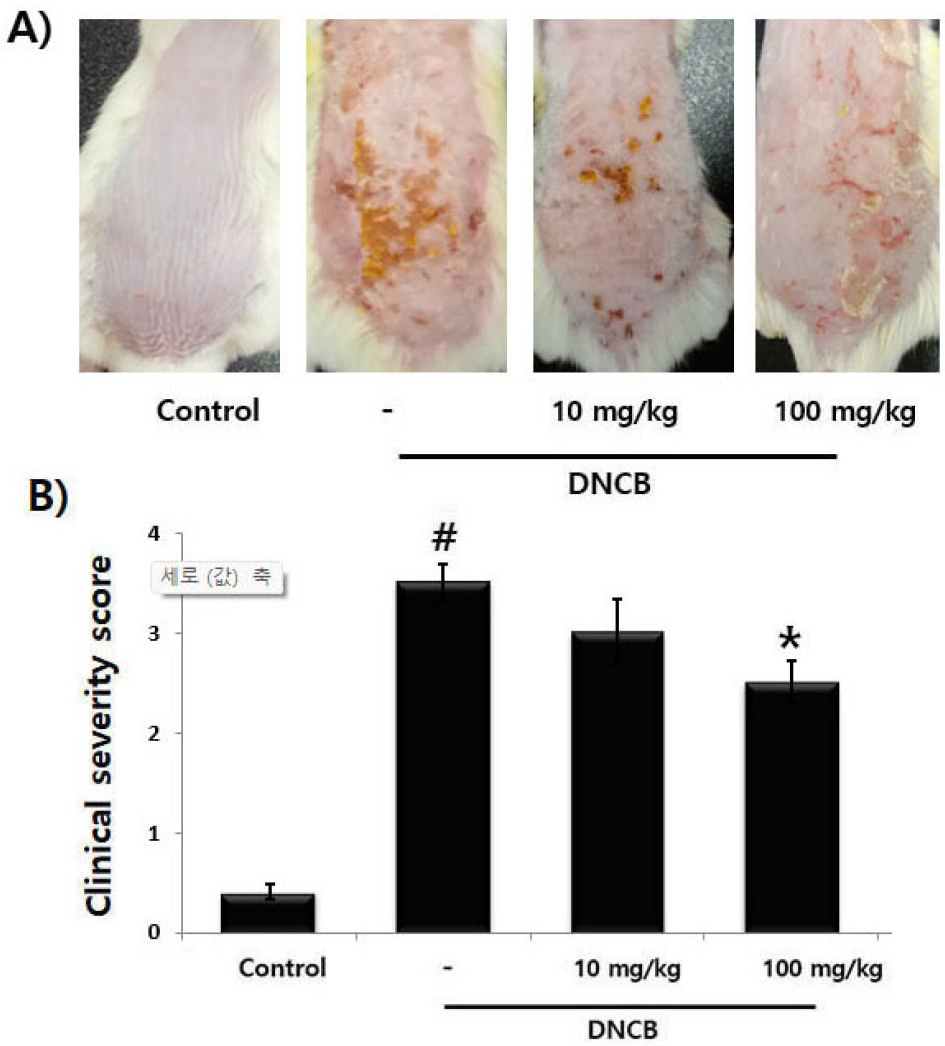
- The Improving Effects of Pu-erh Tea on Atopic Dermatitis in vivo and in vitro
- Su-Jin Kim
- Pu-erh tea, a world-famous tea, has many health-benefit properties including anti-oxidant, anti-cancer and anti-obesity properties. This study aimed to investigate the pharmacological …
- Pu-erh tea, a world-famous tea, has many health-benefit properties including anti-oxidant, anti-cancer and anti-obesity properties. This study aimed to investigate the pharmacological effect of Pu-erh tea on atopic dermatitis (AD) in vivo and in vitro. We investigated the effects of Pu-erh tea on 2, 4-dinitrochlrobenzene (DNCB)-induced AD clinical symptoms in mice. Additionally, we evaluated the effects of Pu-erh tea on the inflammatory cytokine production and nuclear factor-κB (NF-kB) activation in HaCaT cells. The findings demonstrated that Pu-erh tea improved the AD clinical symptoms, such as erythema, skin dryness, eczematous, and inhibited the serum levels of histamine and IgE in DNCB-induced AD model. Moreover, Pu-erh tea attenuated the inflammatory cytokine production and NF-kB activation in HaCa T cells. Collectively, this result suggests that Pu-erh tea could be used as a therapeutic agent for AD treatment. - COLLAPSE
-
Research Article
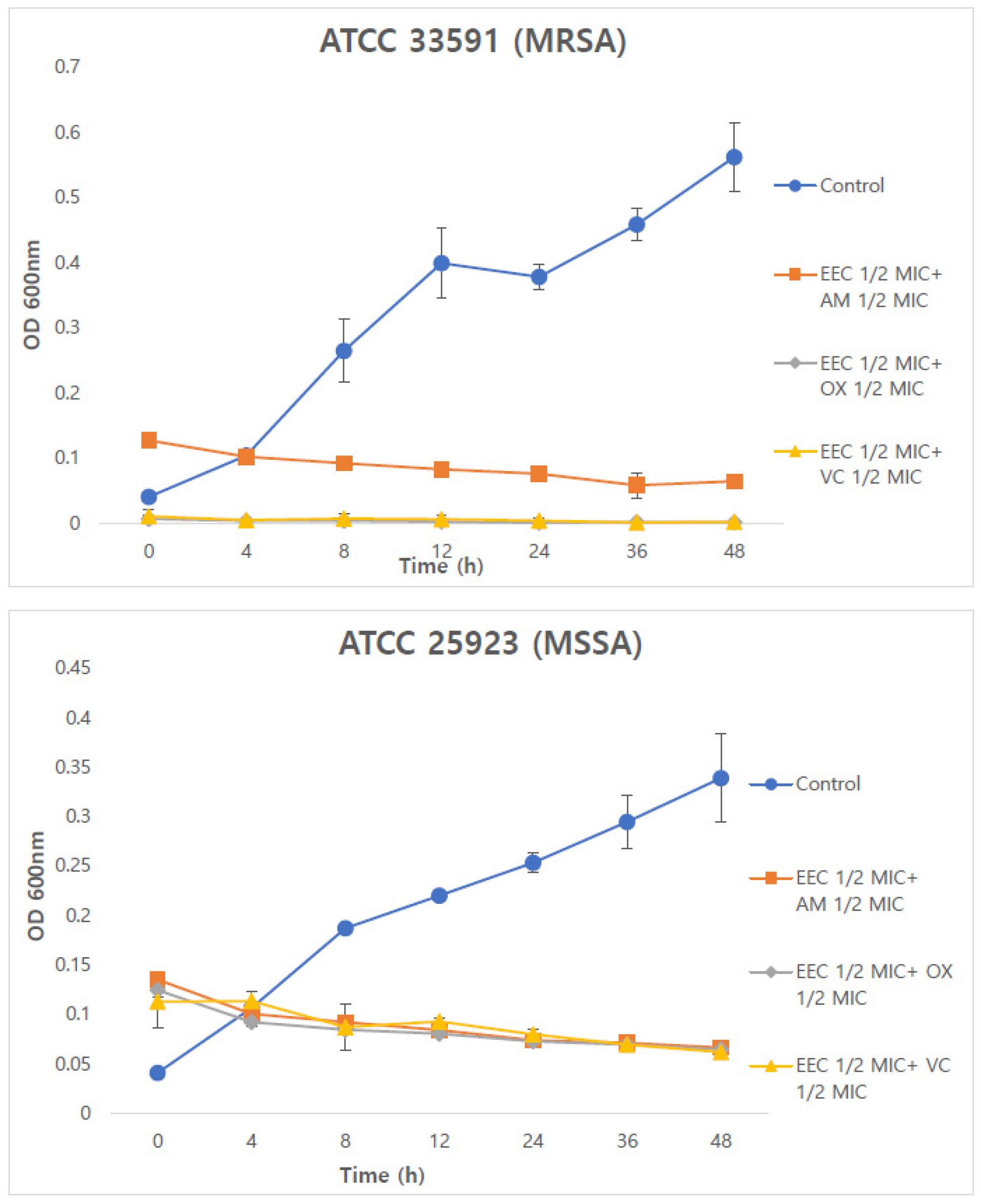
- Antimicrobial Activity of Chamaecyparis obtusa (Siebold & Zucc.) Endl. Xylem Extract against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus
- Ju Yeong So, Dae-Ki Joung, Dong Won Shin
- In this study, the antibacterial activity of Chamaecyparis obtusa (Siebold & Zucc.) Endl. Xylem (COX) was investigated. The antimicrobial activity of the …
- In this study, the antibacterial activity of Chamaecyparis obtusa (Siebold & Zucc.) Endl. Xylem (COX) was investigated. The antimicrobial activity of the EEC was evaluated using minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) tests, colorimetric methods with the MTT assay, checkerboard dilution tests, and by testing against six standard strains of methicillin-resistant S. aureus and one standard methicillin-susceptible S. aureus (MSSA) strain. Chamaecyparis obtusa (Siebold & Zucc.) Endl. is for 7 strains the minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) are in the range of 125-250 ㎍/mL and the FICI values of EEC + AM, EEC + OX and EEC + VC are 0.01-0.03 and 0.04-0.09 and 0.07-0.25 showed an increase in synergy with the checkerboard method performed using MRSA and MSSA strains. When combined together, this effect were dramatically increased. The time-kill curve was measured at OD 600 ㎚ and showed that the number of bacteria was significantly reduced by combining AM, OX and EEC, which dropped below the lowest measurable limit after 48 h. These results demonstrate that Chamaecyparis obtusa (Siebold & Zucc.) Endl. can be a natural antibacterial agent in MRSA. - COLLAPSE
-
Research Article
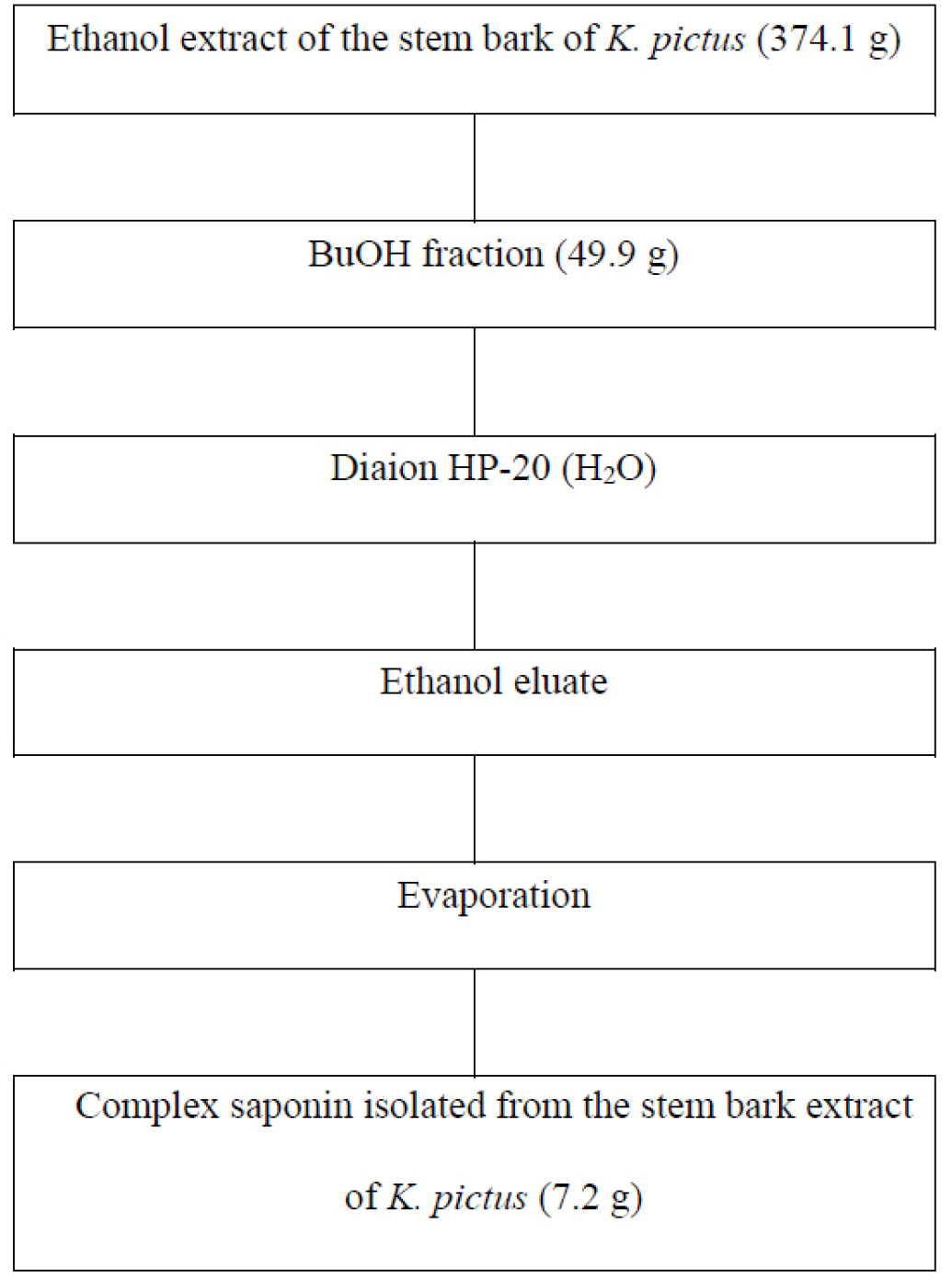
- Vasodilatory Properties of Complex Saponin Isolated from the Stem Bark Extract of Kalopanax pictus
- Jung-Hwan Nam
- The stem bark of Kalopanax pictus contains several bioactive constituents, including syringin, liriodendrin, saponin, and oleanolic acid. The stem bark of K. …
- The stem bark of Kalopanax pictus contains several bioactive constituents, including syringin, liriodendrin, saponin, and oleanolic acid. The stem bark of K. pictus has been conventionally utilized to manage ailments associated with arthritis, hypertension, and hemolysis, in addition to uses associated with its anti-nociceptive and anti-inflammatory characteristics. Nevertheless, the vasodilatory efficacy of complex saponin has yet to be empirically validated within a scientific framework. Consequently, the present investigation examined the vasodilatory properties of complex saponin extracted from K. pictus stem bark in rabbit basilar arteries. For this purpose, arterial rings with both intact and compromised endothelium were employed in an organ bath assay and exposed to endothelin-1 to induce contraction. Complex saponin, identified as the principal active compound within K. pictus stem bark extract, exerted a moderate vasodilatory effect on the basilar arteries of rabbits. Thus, complex saponin derived from K. pictus stem bark extract might preferentially enhance cerebral perfusion through the dilation of the basilar artery. Collectively, the results indicate that complex saponin might potentially be utilized as a vasodilatory agent. - COLLAPSE
-
Research Article
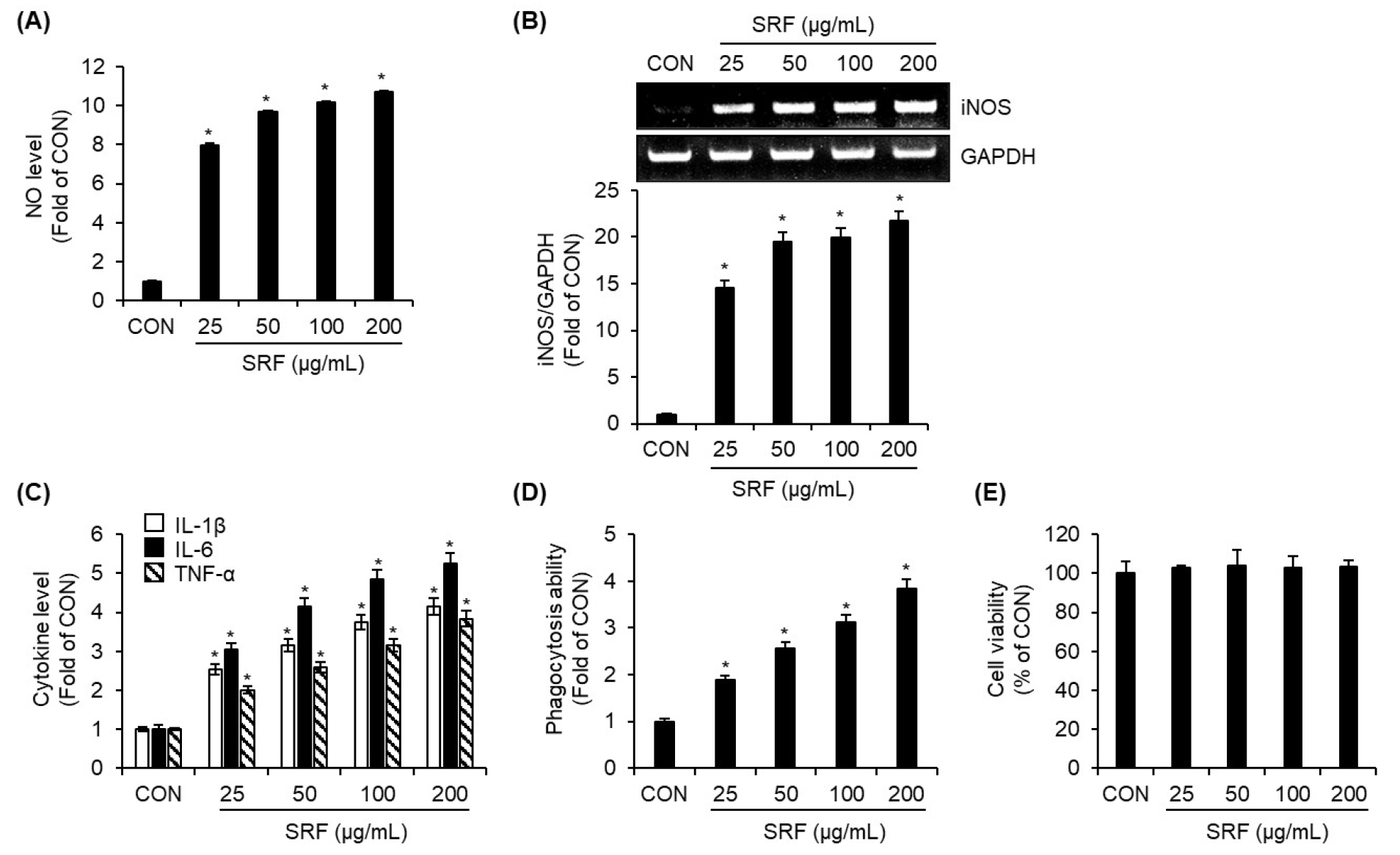
- Immunostimulatory Effects of the Fruits of Sambucus racemosa subsp. pendula via TLR4-mediated ROS/JNK and NF-κB Signaling in RAW264.7 Macrophages
- Gyeong Eun Im, Ji A Kim, Jeong Won Choi, So Jung Park, Hyeok Jin Choi, Min Yeong Choi, Jin Boo Jeong
- This study investigated the immunostimulatory effects of SRF in RAW264.7 macrophages. SRF enhanced NO production, iNOS expression, cytokine secretion (IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α), …
- This study investigated the immunostimulatory effects of SRF in RAW264.7 macrophages. SRF enhanced NO production, iNOS expression, cytokine secretion (IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α), and phagocytic activity without affecting cell viability. Mechanistically, SRF-induced macrophage activation was abrogated by a TLR4 inhibitor but not by a TLR2 inhibitor, indicating TLR4 dependence. Furthermore, JNK and NF-κB signaling pathways were activated by SRF in a TLR4-dependent manner, as shown by inhibitor studies and phosphorylation analysis. SRF also increased intracellular ROS levels via TLR4, and ROS inhibition suppressed SRF-induced JNK and NF-κB activation and subsequent NO production. These findings suggest that SRF activates macrophages through the TLR4-ROS-JNK/NF-κB axis. - COLLAPSE
-
Research Article

- Expression Pattern of Key Genes Involved in Different Pathway Reveal Diversity in Germination and Dormancy in Watermelon
- Nihar Sahu, In-Seong Cho, Su-Won Kim, Ga-Eun Bok, Jong-In Park
- Seed germination and dormancy are complex processes influenced by the seed's physical state, which is affected by environmental factors such as temperature, …
- Seed germination and dormancy are complex processes influenced by the seed's physical state, which is affected by environmental factors such as temperature, soil moisture, light, and nutrient levels. This condition is partly determined by the interplay between the plant's genetic makeup and these external factors. The growth regulator gibberellins (GAs) and abscisic acid (ABA), which conduct opposite metabolic signaling roles that affect seed germination, are responsible. A thorough knowledge of the molecular and biochemical mechanisms controlling these processes is required to fully understand the events occurring in the seed. In this work, we have selected three watermelon cultivars having good germination, moderate germination and low germination percentages. These cultivars were used for the characterization of genes reported to be involved in the germination or dormancy. These genes are involved in different pathways like GA and ABA metabolism and catabolism in plants. Genes responsible for the regulation of germination or dormancy were also used. The interaction between these genes leads to a state of germination or dormancy. The results suggest that DOG1 and CYP707A1 genes, upregulated only in GN3 may be involved in the dormancy. - COLLAPSE
-
Research Article
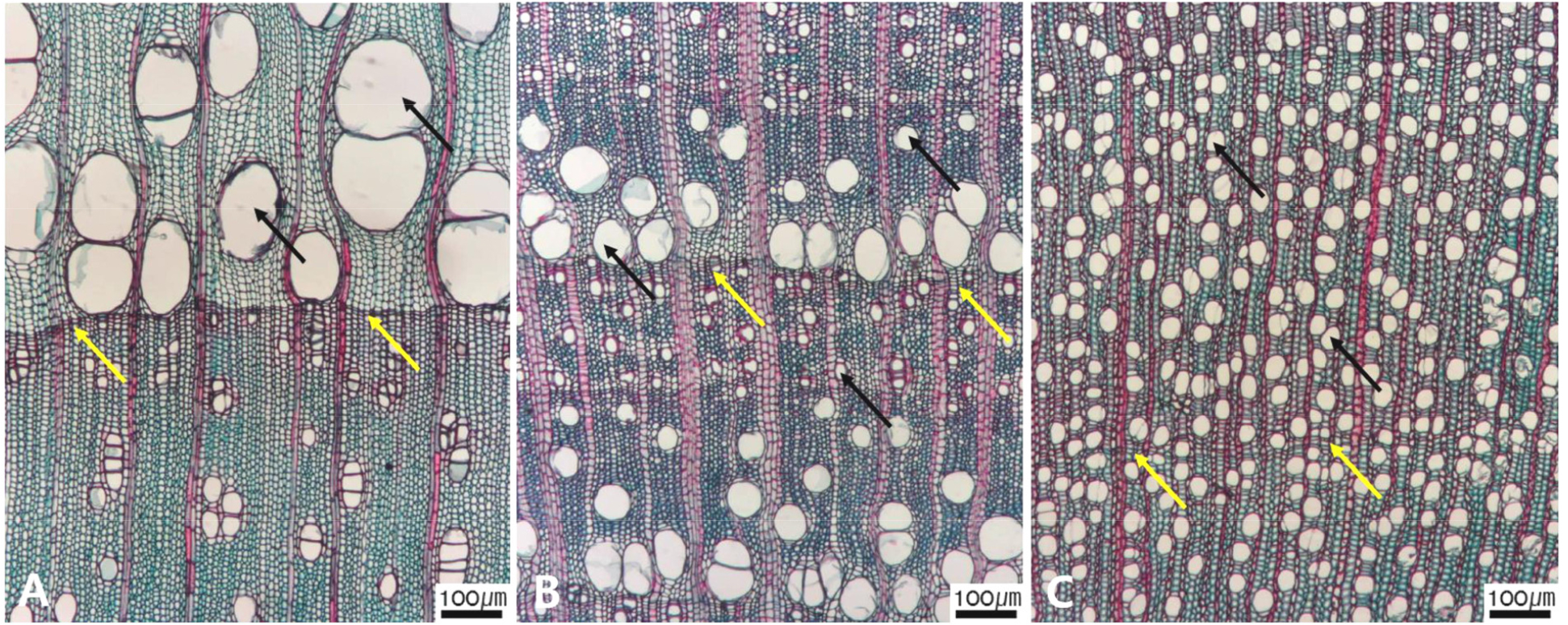
- An Identification Key on Some Korean Angiosperm Sawn Timber: Based on Anatomical Characteristics
- Ji-Na Chu, Sung Soo Whang
- The goal of this study is to create an anatomical key for the sawn timber of 63 species, belonging to 25 families …
- The goal of this study is to create an anatomical key for the sawn timber of 63 species, belonging to 25 families and 63 genera of the Korean angiosperm. After years of the investigation by microscopy, six characters were preferentially selected, significantly important to identify the wood pieces. They are vessel, ray parenchyma, axial parenchyma, tracheid, and fiber cell. They were further divided into few more detailed characters, and then their character states were explained together with micrographs. Based on the data obtained here, we created an anatomical key, making possible to identify species for some Korean woody angiosperm sawn timbers. The results of this study are also expected to serve as reference materials for identifying the various wooden household items collected from both archaeological and paleological sites. - COLLAPSE
-
Research Article
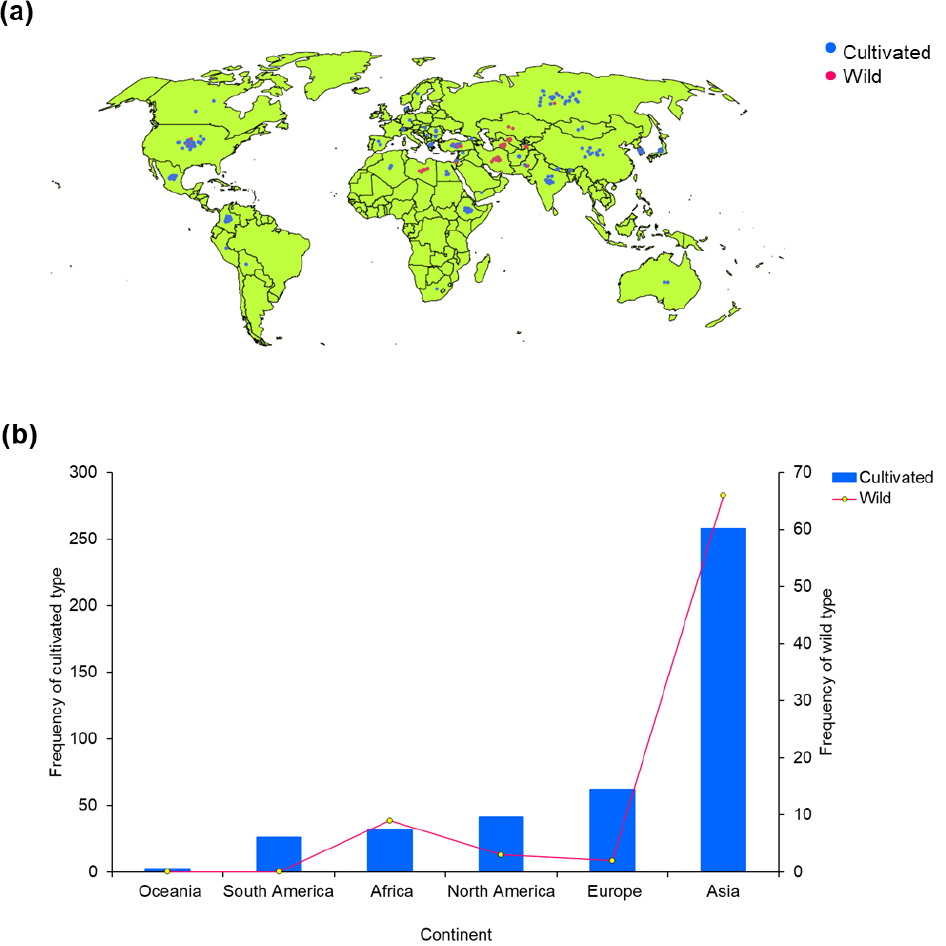
- Agro-morphological Diversity in Global Barley Collections with a Comparative Study of Wild and Cultivated Varieties
- Kebede Taye Desta, Myoung-Jae Shin, Eunae Yoo, Gi-An Lee, Me-Sun Kim, Chong-Tae Chung, Jungyoon Yi, Yu-Mi Choi
- This study examined the agro-morphological diversity of 423 cultivated and 78 wild barley accessions collected from six continents and grown during the …
- This study examined the agro-morphological diversity of 423 cultivated and 78 wild barley accessions collected from six continents and grown during the 2022-2023 winter season in Korea. The use of the standardized Shannon-Weaver index, Chi-square test, and analysis of variance revealed significant variation in both qualitative and quantitative traits. Cultivated types were mainly semi-erect in growth habit (66.19%), while 87.18% of wild types were intermediate. The flag leaf attitude in wild types was mostly horizontal (97.44%), whereas cultivated types commonly had horizontal (47.28%) and semi-erect (32.15%) flag leaves. Wild barley demonstrated stronger cold resistance, with 50.00% being intermediate- resistant and 46.15% semi-resistant. In contrast, 27.90% of cultivated types were susceptible, and 14.42% sustained severe damage. Wild types all had two-rowed spikes and hulled grains, while 77.54% and 13.71% of cultivated types were six-rowed and hulless, respectively. Asian accessions showed the highest proportion of semi-erect growth habit (59.88%), and European accessions were mostly intermediate (51.56%). Cold resistance was strongest among Asian and European accessions, while African accessions were found to be the most susceptible. Quantitative trait analyses revealed that cultivated types had a higher average number of grains per spike compared to wild barley. Conversely, wild barley produced heavier grains (48.40 g) than cultivated types (41.81 g). African accessions were the tallest (108.73 ㎝), while Oceanian accessions were the shortest (70.53 ㎝). Multivariate analysis effectively distinguished accessions by type and region, showing diverse associations among quantitative traits. Overall, this study highlights the agro-morphological variation among wild and cultivated barley genotypes of different origins, identifying nineteen top-performing accessions with desirable qualities. - COLLAPSE
-
Research Article

- Photosynthetic Performance and Growth-related Traits of Petasites japonicus under Different Shading Conditions
- Yu Shin Kwak, Ki Duk Park, Ji Seon Park, Youn Gi Moon, Jae Young Ko, Eun Ju Cheong
- P. japonicus, a perennial herbaceous plant widely consumed as a vegetable in Korea, requires optimized light management during summer cultivation to …
- P. japonicus, a perennial herbaceous plant widely consumed as a vegetable in Korea, requires optimized light management during summer cultivation to ensure stable growth and high-quality yield. This study aimed to evaluate the photosynthetic response and quality traits of P. japonicus under varying shading conditions. Light response curves were measured using a portable gas exchange system and analyzed using three nonlinear regression models: Exponential, Rectangular Hyperbola, and Non-rectangular Hyperbola. Among these, the Exponential model showed the highest predictive accuracy (R2 = 0.9970), suggesting it captures the gradual saturation pattern of photosynthesis. Physiological parameters such as net photosynthetic rate (Pn), dark respiration rate (Rd), light compensation point (LCP), and light saturation point (LSP) decreased significantly with increasing shading intensity, indicating reduced light utilization efficiency under deep shade(95%). In contrast, the 55% shading treatment resulted in the highest fresh weight and leaf area, suggesting improved photosynthetic productivity under moderate shading. However, leaf hardness significantly decreased with higher shading, indicating a trade-off between yield and textural quality. Leaf color analysis revealed that RGB and HSV values were sensitive to shading levels, with Value (V), red (R), and saturation (S) values declining as shading increased. These results suggest that P. japonicus exhibits a shade-tolerant growth strategy, with moderate shading improving biomass and leaf expansion while deep shading suppresses photosynthesis. - COLLAPSE
-
Research Article
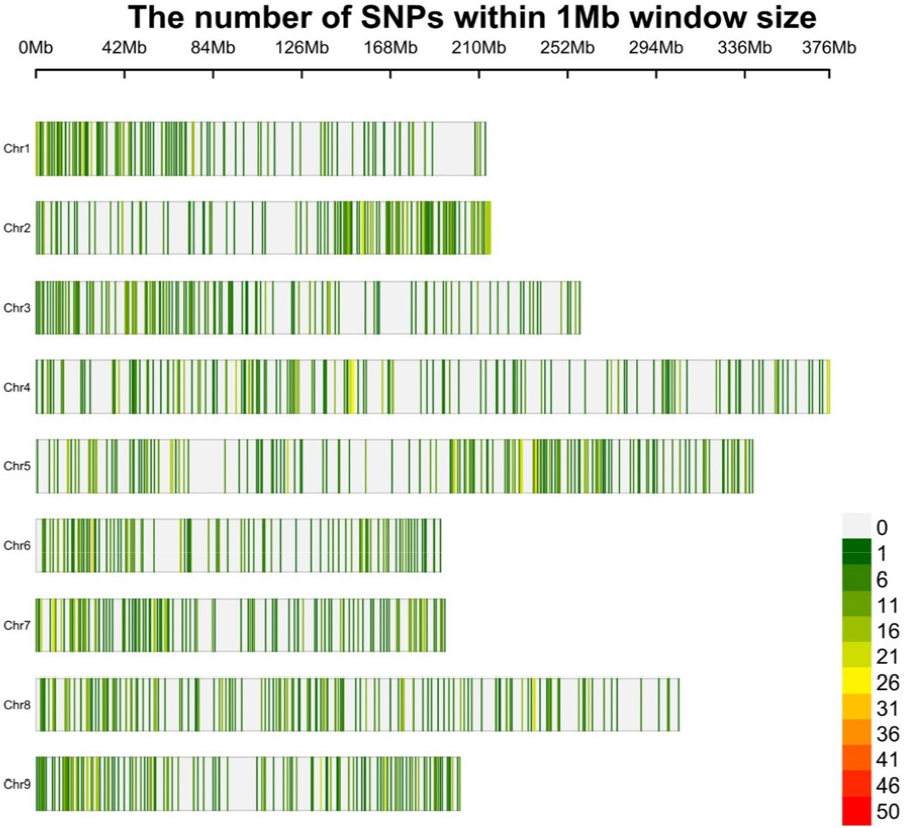
- Genetic Diversity and Phylogenetic Relationships in Wild and Cultivated Lactuca Species
- Suyun Moon, Yoon-Jung Lee, Seong-Hoon Kim, Dae-Won Ki, Bum-Soo Hahn, Aejin Hwang, Hyeonseok Oh, Tae-Sung Kim, Young-Wang Na
- Lettuce (Lactuca sativa) is an economically important leafy vegetable in the family Asteraceae, yet its domestication history and evolutionary relationships …
- Lettuce (Lactuca sativa) is an economically important leafy vegetable in the family Asteraceae, yet its domestication history and evolutionary relationships with wild relatives remain incompletely understood. We used genotyping- by-sequencing to analyze genome-wide variation across 145 accessions representing five Lactuca species (L. indica, L. saligna, L. sativa, L. serriola, and L. virosa). A total of 5,301 high-quality SNPs were identified and used to assess genetic diversity, population structure, and phylogenetic relationships. Among the species, L. virosa exhibited the highest genetic diversity. Analysis of molecular variance showed that 54% of the total genetic variation was distributed among species, indicating substantial interspecific differentiation. Population structure and phylogenetic analyses supported four major clusters with strong concordance across methods. Among the wild taxa, L. serriola and L. virosa were the most genetically similar to cultivated lettuce. Although interspecific divergence was evident, L. sativa showed moderate genetic connectivity with both species. Directional gene flow analysis inferred migration signals from L. saligna to L. virosa and from L. indica to L. serriola, reflecting complex interspecific interactions. These results provide genomic insights into the diversity and relationships among Lactuca species and offer a foundation for future breeding and germplasm conservation. - COLLAPSE
-
Research Article

- An Identification Key on Some Korean Gymnosperm Sawn Timber: Based on Anatomical Characteristics
- Ji-Na Chu, Sung Soo Whang
- The study aims are to create an anatomical key for the sawn timber of 18 species, belonging to seven families and 18 …
- The study aims are to create an anatomical key for the sawn timber of 18 species, belonging to seven families and 18 genera of the Korean gymnosperm. After years of the investigation by microscopy, seven characters were preferentially selected, significantly important to identify the wood pieces. They are intercellular canals/resins duct, axial parenchyma, longitudinal tracheid, ray tracheid, ray parenchyma, cross-field fitting, and ray. They were further divided into few more detailed characters, and then their character states were explained together with micrographs. Based on the above data, we create an identification key for some Korean gymnosperm sawn timber. The results of this study are also expected to serve as reference materials for identifying the various wooden household items collected from archaeological sites. - COLLAPSE
-
Research Article
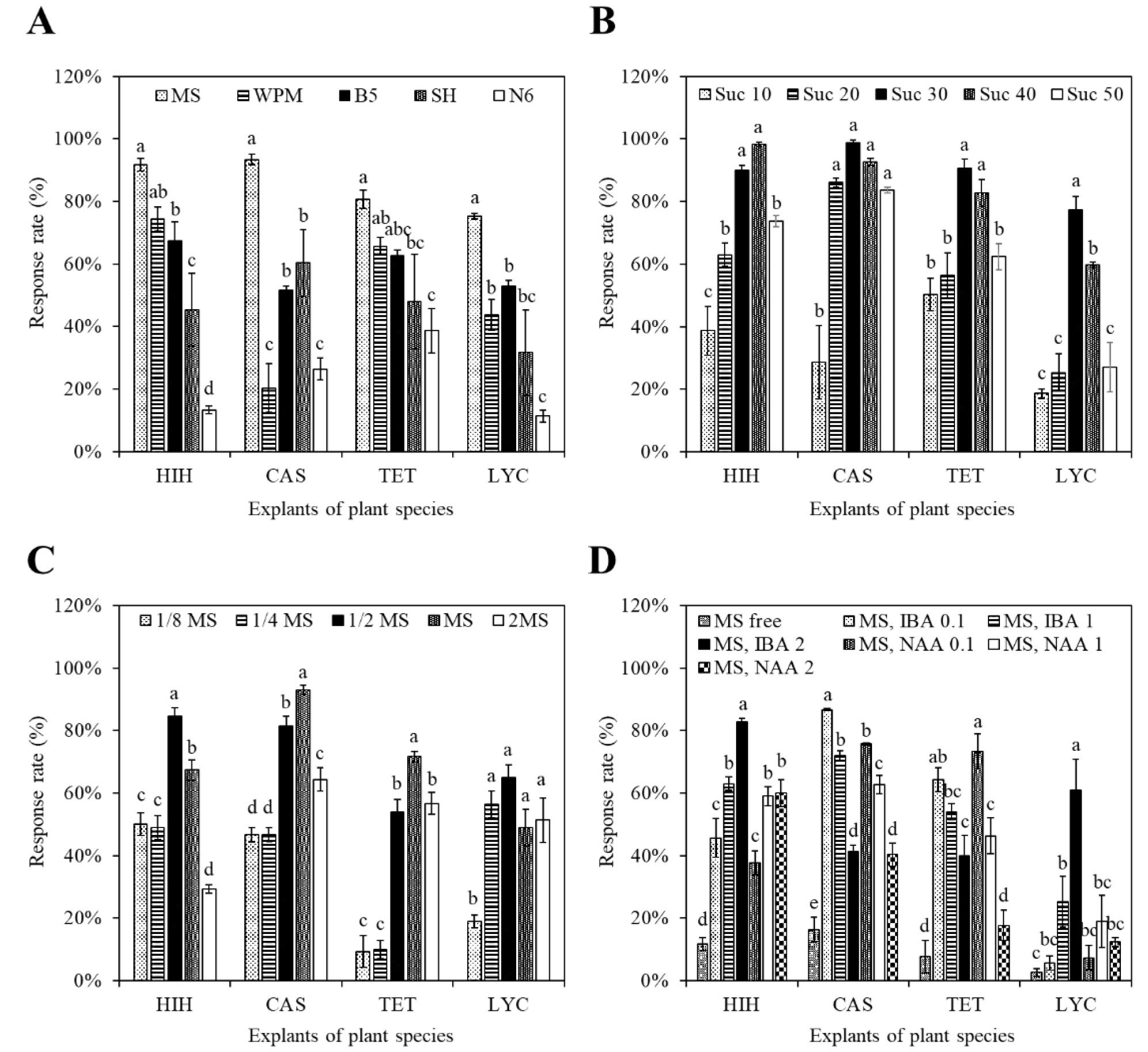
- Optimization of Adventitious Root Culture Conditions and Airlift Bioreactor Scale-Up in Four Jeju Native Plants
- Jong-Du Lee, Eunbi Jang, Weon-Jong Yoon, Young Min Ham, Ji-Gweon Park, So-Young Park, Yong-Hwan Jung
- Jeju Island, a UNESCO World Natural Heritage Site, is rich in native plant diversity. However, many of these plants are underutilized due …
- Jeju Island, a UNESCO World Natural Heritage Site, is rich in native plant diversity. However, many of these plants are underutilized due to propagation challenges and ecological sensitivity. In line with international biodiversity frameworks (CBD and ABS), this study aimed to establish an optimized in vitro adventitious root (AR) culture platform for the conservation and bioutilization of selected Jeju native plants. Extensive surveys and in vitro evaluations identified four high-performance candidates for AR induction, Calystegia soldanella (CAS), Hibiscus hamabo (HIH), Lycoris chejuensis (LYC), and Tetragonia tetragonoides (TET). We systematically optimized culture conditions, finding that Murashige and Skoog (MS) media and specific auxin treatments (IBA and NAA) enhanced rooting efficiency. The most responsive cultures were scaled up in 5 L airlift bioreactors. Biomass performance was quantified by various metrics, including growth index and relative growth rate. CAS and HIH showed superior proliferation, yielding over 30 g DW·batch-1 with a relative growth rate above 3.0. This study successfully optimized a bioreactor-based AR culture platform, demonstrating its technical and biological feasibility for both ex situ conservation and industrial-scale bioproduction. The platform provides a scalable, ESG-aligned model for the genetic preservation and sustainable valorization of Jeju’s unique botanical resources within the emerging bioeconomy. - COLLAPSE
-
Research Article

- Comparison of Growth-Inhibition Effect with Diniconazole Applications on Plug-seedlings Growth in Cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) and Korean Zucchini (Cucurbita moschata L.)
- Jae-pil Jeong, Chang-Hyu Bae
- To promote healthy-seedling growth, the effects of various concentration of diniconazole treatments between foliar spraying and drenching irrigation on growth inhibition of …
- To promote healthy-seedling growth, the effects of various concentration of diniconazole treatments between foliar spraying and drenching irrigation on growth inhibition of plug seedlings were evaluated in cucumber and Korean zucchini. As a result of this research, plant height, hypocotyl length, leaf length and leaf width of all the crop seedlings were decreased significantly as concentration of diniconazole treatment increased in both the foliar spraying and the drenching treatment. At the time of seedling shipment the optimal concentrations were determined to be 20 ㎎/L for foliar application and 1.25 ㎎/L for drench application in cumber, whereas in Korean zucchini, 20 ㎎/L to 37.5 ㎎/L for foliar application, and 1.25 ㎎/L to 2.5 ㎎/L for drenching treatment. The drench application was found to sustain the growth-inhibitory effect on seedlings even at concentrations approximately 16 times lower than those used in foliar spraying. Moreover, the inhibiting effect for seedling growth by the irrigation treatment was sustained until shipment time of the plug seedlings. Thus, the drenching treatment was shown to be more effective than the foliar spraying to raise healthy seedlings between cucumber and Korean zucchini. - COLLAPSE
-
Research Article
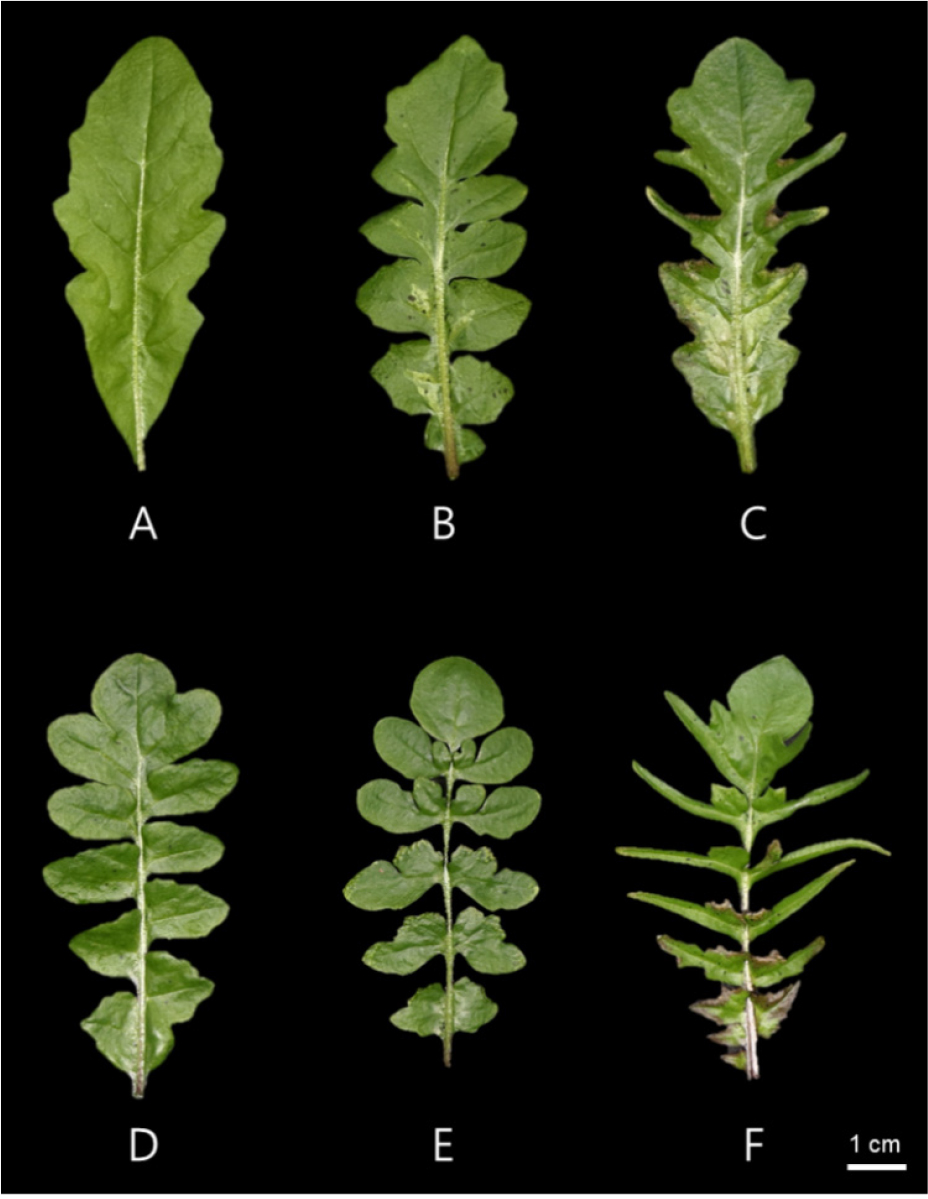

- Trait-Based Clustering Analysis Reveals Phenotypic Diversity and Regional Differentiation in Capsella bursa-pastoris (Shepherd’s Purse)
- Eun-Gyeong Kim, Jae-Eun Lee, Sookyeong Lee, Gi-An Lee
- Morphological diversity and its association with geographic origin are crucial for the conservation and genetic use of Capsella bursa-pastoris (shepherd’s purse). In …
- Morphological diversity and its association with geographic origin are crucial for the conservation and genetic use of Capsella bursa-pastoris (shepherd’s purse). In this study, 35 accessions from Korea and abroad were evaluated using 13 phenotypic traits of shoots and roots. Factor Analysis of Mixed Data (FAMD) and Partitioning Around Medoids (PAM) clustering classified the accessions into six clusters (C1–C6), with C5 and C6 distinctly separated, indicating unique phenotypic compositions shaped by trait combinations or regional origin. Root size-related traits such as length, area, and volume were most pronounced in C1, whereas C6 exhibited the smallest values. C5 showed thicker roots despite shorter lengths, and C4 had the greatest number of root forks and links. Root link length (RLL) was highest in C6, reflecting diverse root architectures. Correlation analysis revealed generally positive relationships among root traits, while RGB and RLL associations varied by cluster, with C5 showing a strong correlation (r = 0.91). Regional composition differed among clusters, and Shannon’s diversity index for leaf-lobed type (LL) was highest in C6 and lowest in C5. These results elucidate phenotypic diversity and population structure in C. bursa-pastoris, supporting efficient germplasm classification and selection for breeding. - COLLAPSE
-
Research Article
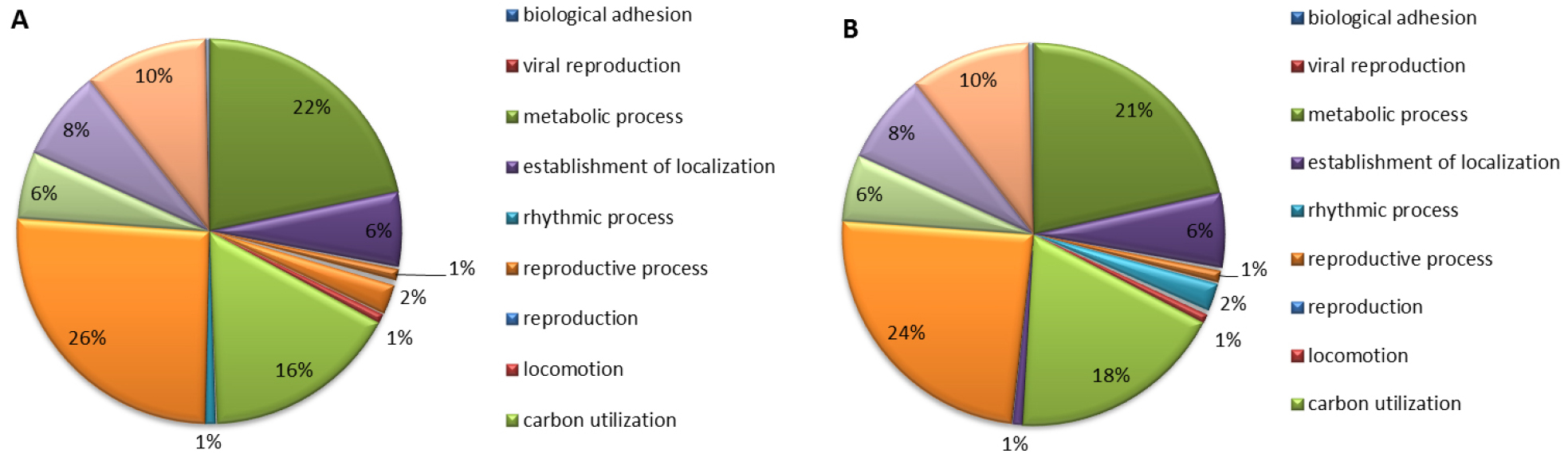
- Development of Transcriptome-Based Single Nucleotide Polymorphism Markers for Pear Skin Color
- Se Hee Kim, Sewon Oh, Sang-Yun Cho, Hyun Ran Kim
- Breeding efficiency in new pear cultivar is considerably low due to long juvenility and self-incompatibility. Therefore, it is necessary to develop early …
- Breeding efficiency in new pear cultivar is considerably low due to long juvenility and self-incompatibility. Therefore, it is necessary to develop early selection markers to screen seedlings with target traits and to increase breeding efficiency. For the comparison of transcription profiles in pear cultivars with different skin color, two cDNA libraries were constructed. Differences in gene expression between red-skinned ‘Rosired Bartlett’ and green-skinned ‘Bartlett’ were investigated by NGS. EST of clones from two cultivars was selected for nucleotide sequence determination and homology searches. MYB10, CHI, and F3H were more predominantly expressed in the red-skinned cultivar rather than the green- skinned cultivar by qRT-PCR. Putative SNPs were screened from pear EST contigs by HRM analysis between ‘Rosired Bartlett’ and ‘Bartlett’. All 21 pairs of SNPs were discriminated and the HRM profiles of amplicons were established. In this study, we report an efficient way to develop two SNP markers for distinguishing between red- and green-skinned pear cultivars by HRM analysis. These SNP markers would be useful for pear marker assisted breeding and provide a good reference for relevant research on molecular mechanisms of color variation in pear cultivars. - COLLAPSE
-
Research Article
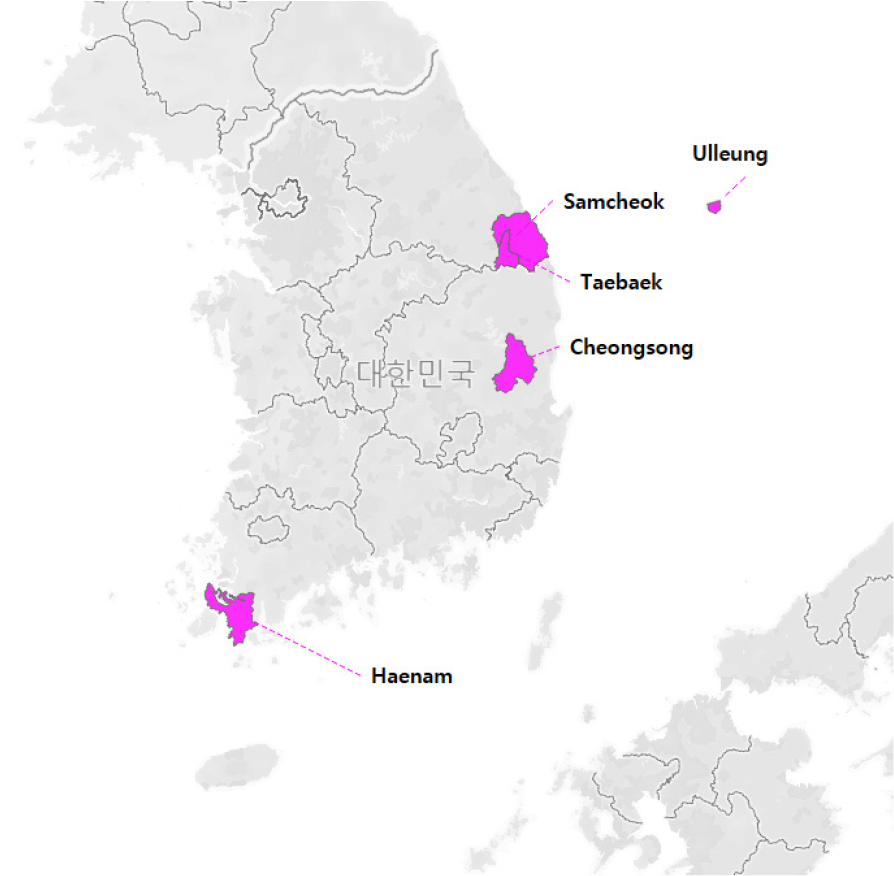
- Genetic Diversity and Population Structure of the Endangered Species Epilobium hirsutum L. (Onagraceae)
- Sunmi Park, PyoungBeom Kim, Sumi Choi, Saeyeon Hwang, SeonJoo Park
- Epilobium hirsutum, classified as an Endangered Species by the Ministry of Environment, is distributed in fewer than five native habitats in …
- Epilobium hirsutum, classified as an Endangered Species by the Ministry of Environment, is distributed in fewer than five native habitats in South Korea. Genetic diversity research on this species is insufficient, and no conservation management plan has been established. in this study, we assessed the taxonomic distinctiveness of the Haenam population and evaluated the genetic diversity and population structure of four E. hirsutum populations. our results revealed generally low haplotype and nucleotide diversity, along with a wide range of genetic differentiation among populations (Pairwise-FST). Furthermore, analysis of molecular variance (AMOVA) indicated that most genetic variation was distributed within populations rather than among them. these findings underscore the urgent need for both in situ and ex situ conservation strategies to preserve the genetic diversity of E. hirsutum. On the other hand, our matK-based phylogenetic analysis showed that the Haenam population formed a distinct monophyletic clade with high bootstrap support, suggesting that it may be more closely aligned with E. parviflorum than with E. hirsutum. - COLLAPSE
-
Research Article
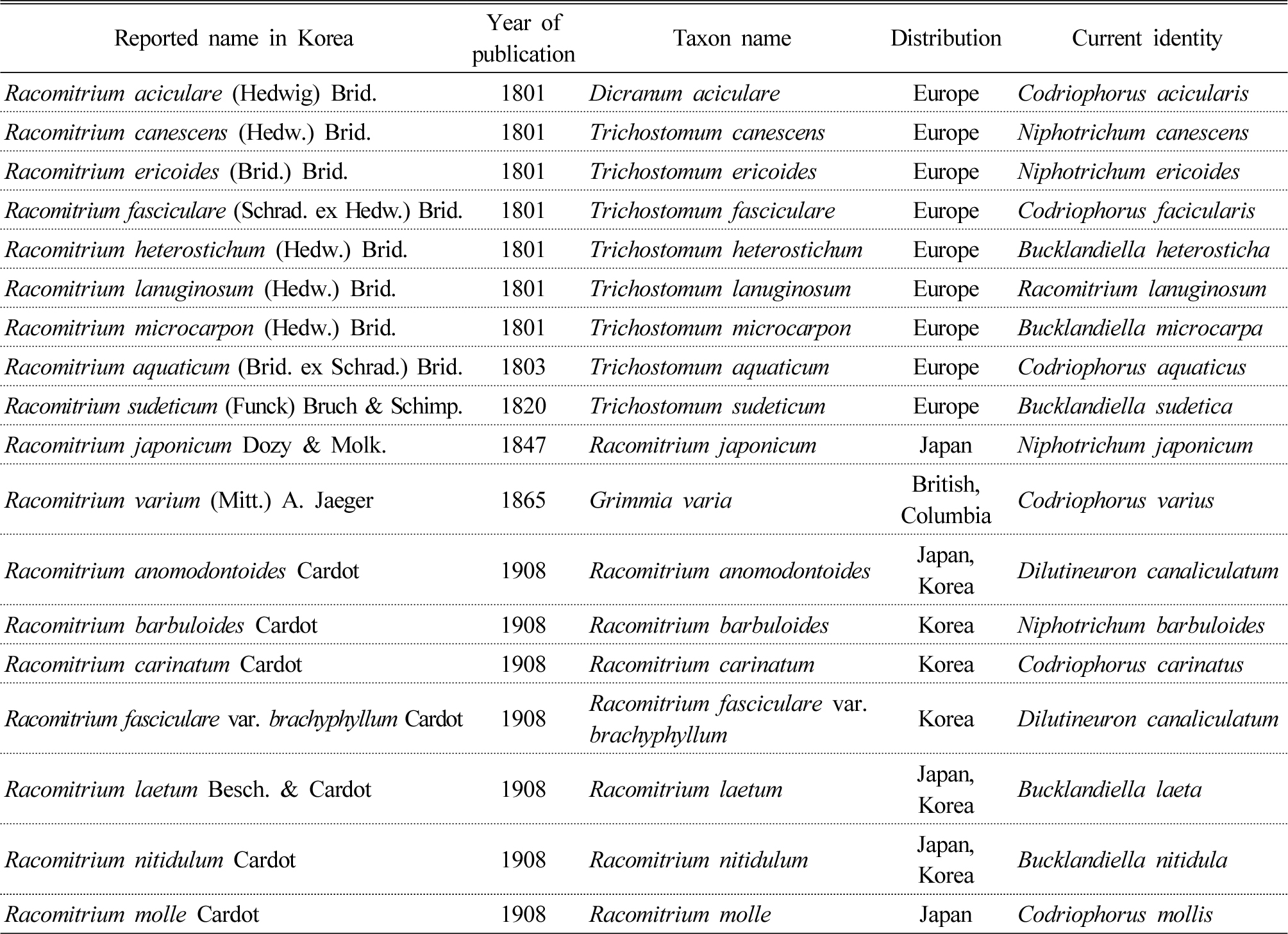
- Microhabitat Analysis on the Genus Racomitrium from East Asia
- Eunhwa Yoo, Kyounghoon Kim, JeeEun Koo, Shin-Ho Kang
- The genus Racomitrium, a genus of mosses in the family Grimmiacea has traditionally been used for landscaping and as packing materials. …
- The genus Racomitrium, a genus of mosses in the family Grimmiacea has traditionally been used for landscaping and as packing materials. Recently, it has been getting attention as resources plants with excellent carbon reduction capabilities and response capabilities to the climate crisis in Korea. As interest in Racomitrium mosses as a resource plant increases for indoor landscaping in Korea, there is also an increasing demand for information on the environmental elements for acculturation as well as morphological characteristics of native Racomitrium mosses. This study analyzed approximately 3,515 herbarium specimen labels from 97 institutions, including data from across East Asia (Korea, Japan, China, Taiwan), to determine species-specific habitat preferences regarding altitude, topography, light, moisture, and substrata. Therefore, this study aimed to understand ecological characteristics of the Genus Racomitrium in Korea that could be used as a resource plant, and to identify the distribution and habitat characteristics. - COLLAPSE
-
Research Article

- Photoperiod Optimization in Controlled Environments: Interspecific Differences in Vegetative Growth and Photochemical Efficiency among Three Phedimus Species Native to Korea
- Jae Hwan Lee, Samuel Lee, Jeong Geun Lee, Seon Yong Hwang, Sang Yong Nam
- In this study, we investigated changes in vegetative growth and photochemical efficiency in three native Korean Phedimus species under four different photoperiods: …
- In this study, we investigated changes in vegetative growth and photochemical efficiency in three native Korean Phedimus species under four different photoperiods: 8, 10, 12, and 14 h·d-1. The longest photoperiod (14 h·d-1) simultaneously improved vegetative growth and photochemical efficiency (Fv/Fm and PIABS) in P. takesimensis, whereas P. latiovalifolium exhibited a pronounced enhancement in plant quality indices (compactness and Dickson quality index). In P. zokuriensis, root length and several stress indicators (ΦDo, ABS/RC, and DIo/RC) increased under the shortest photoperiod (8 h·d-1), suggesting that the optimization of organ-specific development (shoot vs. root growth) and the balance between photochemical efficiency and physiological stress should be considered together. In controlled environments, a species-tailored photoperiod strategy appears appropriate, aiming to maintain or improve Fv/Fm and PIABS while suppressing excessive increases in ABS/RC, DIo/RC, and ΦDo. As these findings were based on an evaluation of photoperiod as a single factor, further validation that includes the interactions between light quality, light intensity, and temperature is warranted. Overall, the results of this study provide insights into species-specific responses to photoperiod and outline strategies for differentiating cultivation settings among congeneric species. - COLLAPSE
-
Research Article
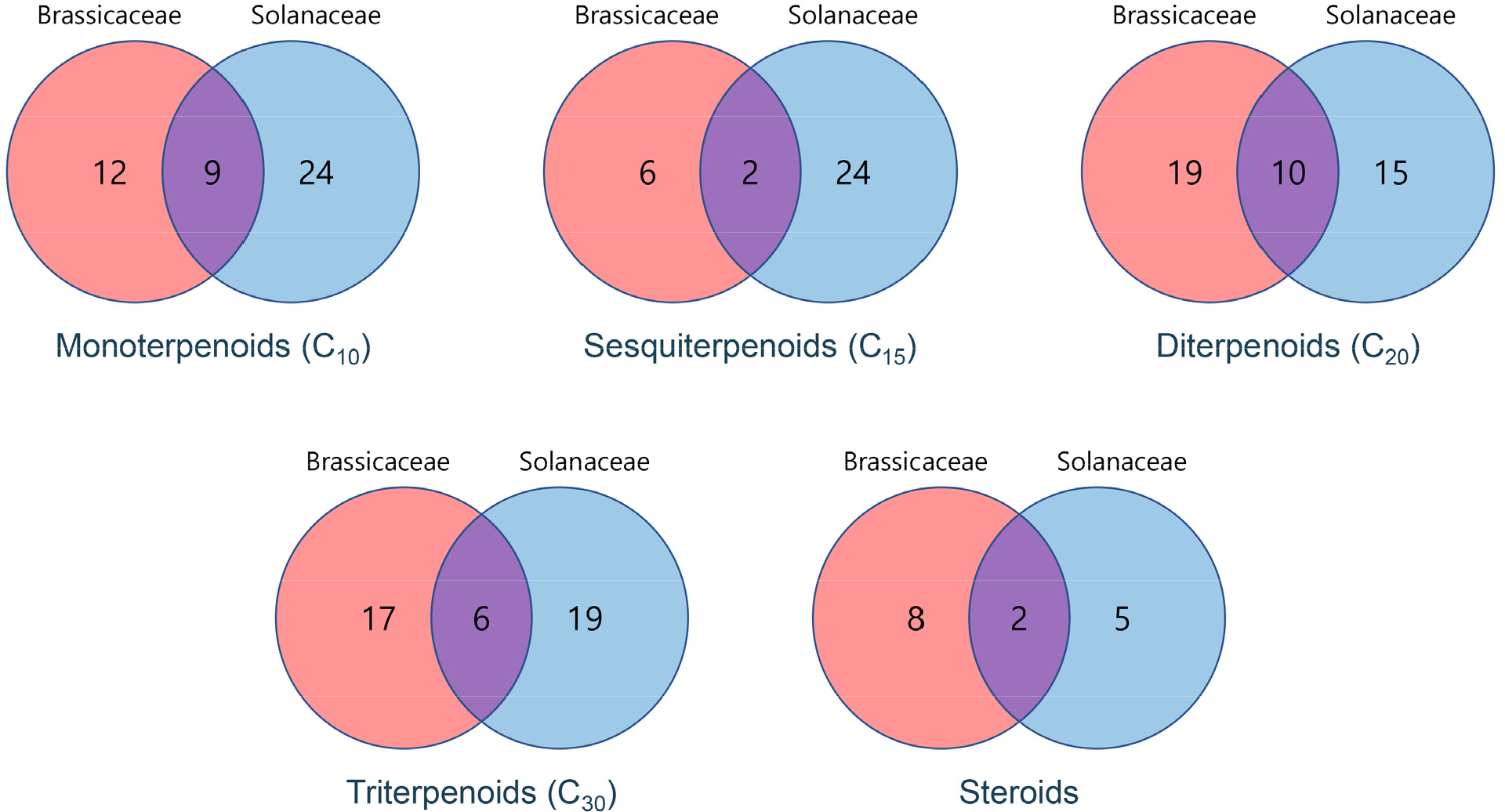
- Cross-talks of Terpenoids Between Brassicaceae and Solanaceae Plants
- Ui-Lim Choi, Mi Hee Kim, Dong-Uk Shin, Kangmin Kim, Gun Woong Lee
- Terpenoids are ubiquitous throughout the plant kingdom and fulfill diverse biological roles, such as allelopathy, insect-plant interactions, cross-talk with plant hormones, and …
- Terpenoids are ubiquitous throughout the plant kingdom and fulfill diverse biological roles, such as allelopathy, insect-plant interactions, cross-talk with plant hormones, and the modulation of biotic and biotic stress responses. These versatile functions highlight their significance in plant growth, development, and adaptation as well as their potential applications in the agriculture, food, and pharmaceutical industries. In this review, we systematically surveyed plant secondary metabolite databases to extract and compare terpenoids reported in two agriculturally important plant families, Brassicaceae (Cruciferae) and Solanaceae. We focused on monoterpenes, summarize their occurrence, and outlined their biological and ecological functions. Based on information across families, we highlighted both shared and unique terpenoids, which provided insights into their ecological roles and evolutionary significance. Furthermore, we discussed how cross-family perspectives on terpenoid-mediated signaling and communication suggest potential strategies to enhance crop performance and environmental resilience in the future. This review underscores the novelty of comparative family level analysis of terpenoids and offers an integrative framework for utilizing these metabolites in plant science and applied research. - COLLAPSE
Journal Informaiton
 Korean Journal of Plant Resources
Korean Journal of Plant Resources
Journal Informaiton
Journal Informaiton - close
 Korean Journal of Plant Resources
Korean Journal of Plant Resources










