-
Research Article
-
Comparison of Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Five Native Korean Aster Species Depending on Drying Methods
건조방법에 따른 국내 자생 쑥부쟁이속 5종의 항산화 및 항염 활성 비교
-
Hamin Lee, Kyungtae Park, Bo Kook Jang, Seung Youn Lee, Ju-Sung Cho
이하민, 박경태, 장보국, 이승연, 조주성
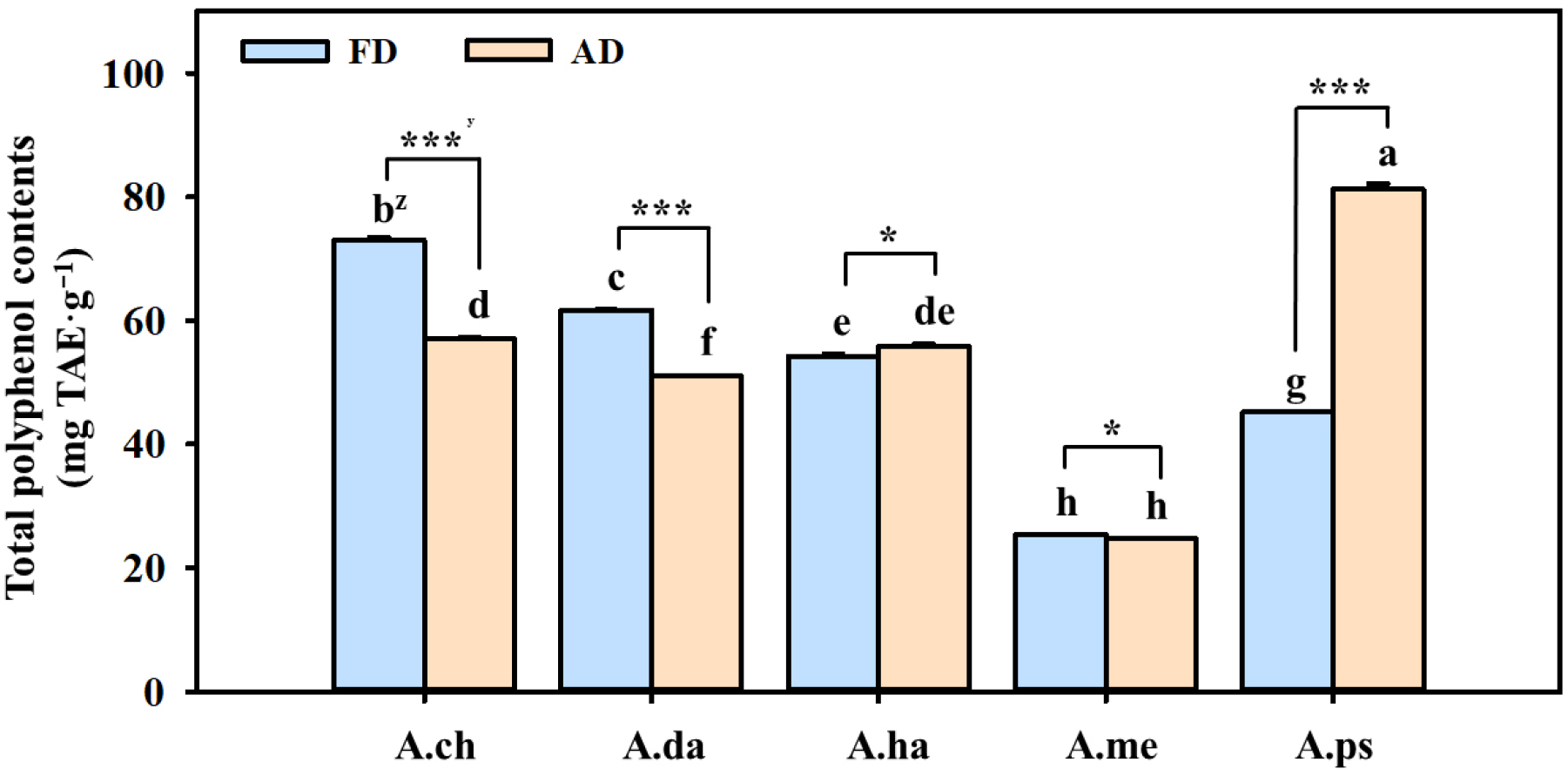
- In this study, the antioxidants and anti-inflammatory activities of five Aster species were compared under two drying methods: freeze-drying (FD) and air-drying …
- In this study, the antioxidants and anti-inflammatory activities of five Aster species were compared under two drying methods: freeze-drying (FD) and air-drying (AD). Each sample was extracted using 50% ethanol for 45 minutes via ultrasonic extraction, a condition optimized through preliminary experiments. Extraction yield differed significantly depending on species and drying method. Total polyphenol and flavonoid contents were higher in Aster × chusanensis (FD: 73.0 ㎎ TAE·g-1; 55.5 ㎎ NE·g-1) and A. danyangensis (FD: 61.7 ㎎ TAE·g-1; 42.6 ㎎ NE·g-1) under FD than under AD, whereas the opposite trend was observed in A. pseudoglehnii (AD: 81.2 ㎎ TAE·g-1; 72.8 ㎎ NE·g-1) and A. hayatae (AD: 55.9 ㎎ TAE·g-1; 39.4 ㎎ NE·g-1), which showed higher levels following AD treatment. DPPH and ABTS radical-scavenging activities also displayed species-specific responses depending on the drying method. In the anti-inflammatory assay, nitric oxide (NO) production was inhibited to different extents depending on both species and drying methods. These findings indicate that even within the same genus, the preservation and enhancement of bioactivity can differ substantially depending on intrinsic species characteristics and drying processes. This study underscores the importance of drying methods in maximizing bioactive properties for the development of functional foods and bio-health ingredients. - COLLAPSE
-
Comparison of Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Five Native Korean Aster Species Depending on Drying Methods
-
Research Article
-
Comparative Analysis of Antioxidant and Anti-inflammatory Activities of Okhwang 1ho (Abeliophyllum distichum Nakai) Flower Extracts Prepared with Different Solvents
미선나무 (Abeliophyllum distichum Nakai, 옥황1호) 꽃 용매별 추출물의 항산화 및 항염증 활성 평가
-
Yong-Shin Kim, Jae Ho Park
김용신, 박재호
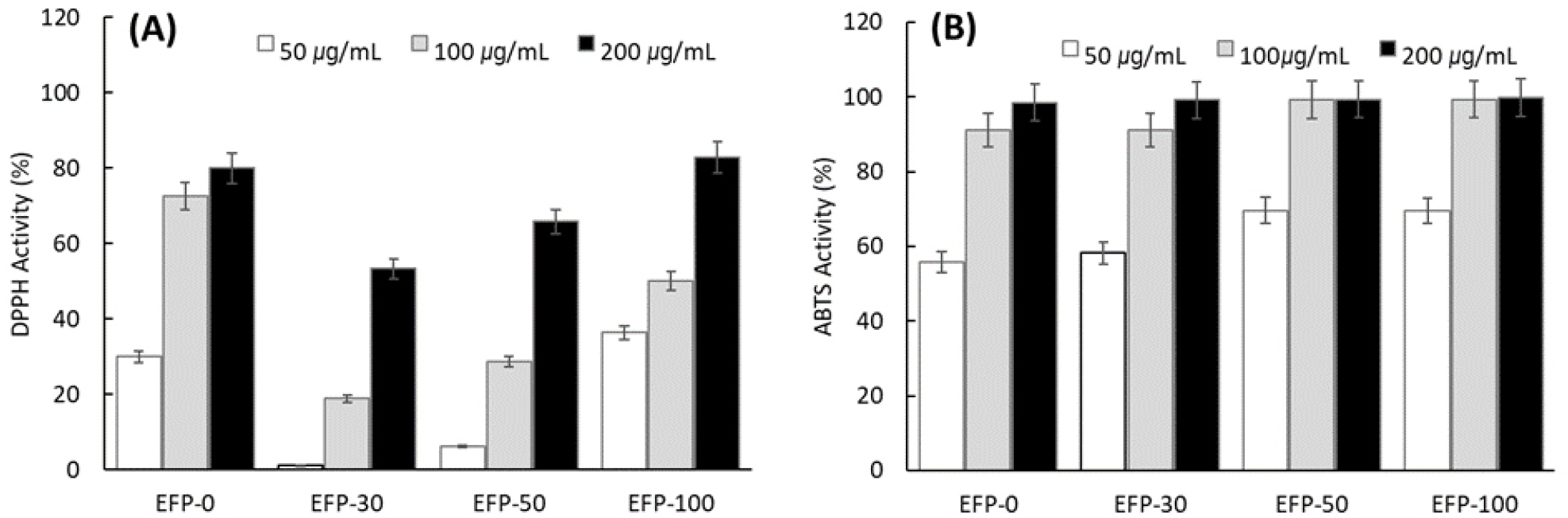
- This study examined the solvent-dependent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of Okhwang 1ho (Abeliophyllum distichum) flower extracts prepared with varying ethanol …
- This study examined the solvent-dependent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of Okhwang 1ho (Abeliophyllum distichum) flower extracts prepared with varying ethanol concentrations (EFP-0, EFP-30, EFP-50, and EFP-100). Radical scavenging capacity was assessed via DPPH and ABTS assays (50~200 ㎍/mL). All extracts demonstrated marked antioxidant activity at low concentrations, while EFP-30 and EFP-50 exhibited superior activity, implying efficient extraction of moderately polar phenolic constituents. Total phenolic content was highest in EFP-50, whereas total flavonoid content increased with ethanol concentration. HPLC profiling confirmed distinct phytochemical signatures: EFP-0 contained rutin, caffeic acid, and acteoside, while EFP-30 and EFP-50 additionally contained isoquercitrin and isoacteoside. In RAW 264.7 macrophages, no cytotoxicity was observed up to 200 ㎍/mL. Under LPS-induced inflammatory conditions, EFP-50 and EFP-100 significantly suppressed NO production, consistent with phenolic/flavonoid enrichment. Western blot analysis further verified downregulation of iNOS and COX-2 expression, indicating inhibition of inflammatory signaling. Collectively, these findings demonstrate that the biological activities of A. distichum flower extracts are strongly influenced by solvent polarity, with 30~50% ethanol yielding optimal bioactive profiles. The study supports the potential application of A. distichum flowers as functional ingredients in health-promoting products. - COLLAPSE
-
Comparative Analysis of Antioxidant and Anti-inflammatory Activities of Okhwang 1ho (Abeliophyllum distichum Nakai) Flower Extracts Prepared with Different Solvents
-
Research Article

-
Rooting Characteristics of Camellia japonica L. by Cutting type, Rooting Medium, and Plant Growth Regulator Treatments
삽목 시기, 토양 종류 및 생장조절제 처리에 따른 동백나무 발근 특성
-
Woo-Jin Jang, Sol-bi Lim, Woo-sol Jeong, Seong-chan Yoo, Young-ki Kim
장우진, 임솔비, 정우솔, 유성찬, 김영기
- This study aimed to optimize a mass propagation system for Camellia japonica by evaluating rooting responses to cutting type (hardwood vs. softwood), …
- This study aimed to optimize a mass propagation system for Camellia japonica by evaluating rooting responses to cutting type (hardwood vs. softwood), rooting medium (sand, Kanumatsuchi, and mixed medium), and plant growth regulators treatment (IBA, NAA × 0, 100, 500, 1,000 ㎎·L-1). Rooting performance differed significantly among treatments. In hardwood cuttings, the highest rooting rate (55.6%) was obtained in Kanumatsuchi with IBA or NAA at 1,000 ㎎·L-1. In softwood cuttings, sand medium treated with IBA at 1,000 ㎎·L-1 resulted in the highest rooting rate (75.6%), whereas mixed medium showed severe decay. Root development characteristics differed significantly among treatments. Overall, softwood cuttings exhibited more vigorous root growth than hardwood cuttings, although their rooting percentages tended to be relatively unstable. Considering both rooting percentage and root development traits, the use of softwood cuttings treated with IBA at 1,000 ㎎·L-1 in sand was determined to be the most suitable and reliable method for improving the propagation success of Camellia japonica. - COLLAPSE
-
Rooting Characteristics of Camellia japonica L. by Cutting type, Rooting Medium, and Plant Growth Regulator Treatments
-
Research Article

-
Deep Learning Based Dry Weight Prediction of Rare Plant Persicaria chinensis (L.) H. Gross
딥러닝 기술을 활용한 희귀식물 덩굴모밀의 건중량 예측
-
Daeho Choi, Jungmok Kang, Yong-Woo Park
최대호, 강정목, 박용우
- This study developed image-based deep learning models for non-destructive prediction of leaf and stem dry weight of Persicaria chinensis and compared the …
- This study developed image-based deep learning models for non-destructive prediction of leaf and stem dry weight of Persicaria chinensis and compared the performance of different convolutional neural network (CNN) architectures. P. chinensis is a rare species designated by the Korea Forest Service with high potential for medicinal and functional food applications, highlighting the need for efficient yield prediction methods. A baseline CNN and four transfer learning models (VGG16, ResNet50, DenseNet121, and MobileNetV2) were evaluated using leaf and stem images as input data. Ten percent of the dataset was reserved as an independent test set, while the remaining data were used for training and validation through K-fold cross-validation (K = 5). Data augmentation and early stopping were applied to improve model generalization. For leaf dry weight prediction, DenseNet121 achieved the highest test performance (R2 = 0.89). For stem dry weight prediction, VGG16 achieved the highest coefficient of determination on the independent test set (R2 = 0.91). Performance differences were attributed to variations in morphological and visual characteristics between leaves and stems. These results demonstrate the feasibility of image-based deep learning for non-destructive yield prediction of P. chinensis in precision agriculture and smart forestry. - COLLAPSE
-
Deep Learning Based Dry Weight Prediction of Rare Plant Persicaria chinensis (L.) H. Gross
Journal Informaiton
 Korean Journal of Plant Resources
Korean Journal of Plant Resources
Journal Informaiton
Journal Informaiton - close
 Korean Journal of Plant Resources
Korean Journal of Plant Resources










